In the construction and logistics industries, end dump trailers have become the workhorse for transporting bulk materials like aggregates, coal, demolition debris, and agricultural products. Their hydraulic lifting systems enable efficient unloading, but this same feature introduces unique operational risks that demand respect and proper training. This guide provides a systematic approach to safe and efficient end dump trailer operation.
Section 1: Pre-Trip Inspection—Your First Line of Defense
A thorough inspection before each trip prevents roadside breakdowns and accidents. Follow this systematic checklist:
Exterior and Structural Inspection
- Body cleanliness: Remove residual materials from previous loads to prevent corrosion and cross-contamination during the next haul
- Paint and structure: Check for cracks, deformations, and ensure weld joints—especially where the body meets the chassis—remain intact
- Locking mechanisms: Verify that side panels and tailgate latches operate properly to prevent accidental opening during transit
Critical Chassis Components
- Tire system: Check for equal tire pressure (uneven pressure causes weight shift during dumping) and inspect tread wear, bulges, or cracks
- Brake system: Inspect brake pad thickness and fluid levels. For air brake systems, test for leaks (dump trucks require air dryer cartridge replacement every 30,000 km)
- Suspension: Check shock absorbers for leaks and inspect leaf springs for cracks, ensuring equal height on both sides
Hydraulic System—The Heart of the Operation
The hydraulic system requires special attention:
- Fluid condition: Check hydraulic oil level and quality. Replace immediately if emulsified or discolored
- Leak inspection: Examine hydraulic cylinders, hoses, and fittings for seepage. Pay attention to high-pressure line aging
- No-load test: Perform 2-3 empty lift cycles to check for synchronized cylinder movement, sticking, or unusual noises
- Control valve: Verify manual and air controls function properly for raise, hold, and lower positions
Electrical and Connection Systems
- Inspect fifth wheel coupling and kingpin wear, ensuring positive locking
- Confirm all lights (brake, turn signal, reverse) operate correctly
- Check electrical harnesses and air lines for damage

Section 2: Loading Operations—Weight Distribution Determines Safety
Loading Principles
- Never overload: Strictly adhere to rated capacity. Overloading stresses hydraulics and increases rollover risk
- Even distribution: Spread material uniformly across the bed. For poorly flowing materials (wet clay), reduce load volume and concentrate slightly toward the rear
- Center of gravity: Place heavier items toward the front (near the tractor), but never exceed the fifth wheel's rated capacity
Special Material Handling
- Sticky materials: Consider bed liners or coatings to reduce adhesion
- Free-flowing materials: Control loading speed for sand or grain to prevent excessive pile height
- Large debris: For rocks or demolition waste, use protective bedding to prevent sharp edges from puncturing the floor
Section 3: On the Road—Anticipatory Driving is Essential
Starting and Driving
- Warm-up procedure: Idle diesel engines for 3-5 minutes until coolant reaches 45°C before moving
- Gear selection: Shift appropriately for conditions. Listen to engine sounds to detect shifting cargo
- Cornering caution: Due to high center of gravity, reduce speed before turns and avoid sharp steering inputs to prevent rollover
Special Road Conditions
- Rough terrain: Reduce speed to prevent violent cargo movement that shifts the center of gravity
- Grades: Build momentum before ascending; never coast downhill in neutral—use engine braking
- Crosswinds: End dump trailers present large side areas. High winds can push the trailer sideways—maintain firm steering and reduce speed
Section 4: Unloading—The Highest Risk Operation
Unloading represents the most dangerous phase of end dump trailer operation. Strict adherence to this protocol is mandatory:
Site Selection and Assessment
- Ground conditions: Must be firm and level with no side slopes. Soft ground causes wheel sinkage and potential rollover
- Slope limitations: Ideally, use perfectly flat ground. If sloped unloading is unavoidable, position the tractor facing downhill—never unload against the grade
- Clearance: Ensure no overhead power lines, branches, or structures. Establish a 10-meter safety perimeter around the unloading zone
Pre-Unloading Preparation
- Unlock tailgate: Ensure complete release to prevent pressure buildup and explosive opening
- Straight alignment: Keep tractor and trailer in a straight line. Avoid "jack-knife" angles where a trailer rollover could crush the cab
- Wheel chocks: When possible, place chocks before and behind wheels to prevent movement
Lifting Protocol
- Staged lifting: Never raise to maximum height immediately. Use 2-3 stages:
- Lift partially and pause
- Check for vehicle tilt
- Monitor tire sinkage
- Verify hydraulic pressure remains normal
- Controlled speed: Raise slowly, allowing material to gradually slide rearward. Rapid lifting causes sudden weight transfer and rollover
- Continuous monitoring: Use mirrors or side windows to observe. Ideally, have a spotter at a safe distance
Emergency Stop Indicators
Immediately stop lifting and lower slowly if you observe:
- Vehicle tilting to one side
- Noticeable tire sinkage on either side
- Unusual hydraulic noise or vibration
- Sudden wind gusts
Post-Unloading Procedures
- Confirm empty: Ensure complete discharge to prevent shifting residual material
- Controlled lowering: After pressing the lower button, confirm the bed fully seats and cylinders completely retract before moving
- Secure locks: Verify side panels and tailgate are fully latched
Section 5: Winter Operations
Cold weather introduces additional challenges:
- Hydraulic preheating: Cold oil increases viscosity. Idle to warm hydraulics or switch to low-pour-point hydraulic fluid
- Snow removal: Clear accumulated snow from bed tops and sides before lifting to prevent sudden slides that affect visibility or balance
- Brake system: Drain air tank moisture to prevent freeze-ups; verify dryer operation
- Traction: Use tire chains on ice, but remove before unloading to prevent damage to tires and ground surfaces
Section 6: Maintenance—The Economics of Longevity
Systematic maintenance dramatically reduces lifecycle costs:
Daily Maintenance
- Clean vehicle; check tire pressure and condition
- Verify hydraulic, brake, and coolant fluid levels
- Test lights, horn, and brake performance
- Perform no-load lift tests
Scheduled Service Intervals
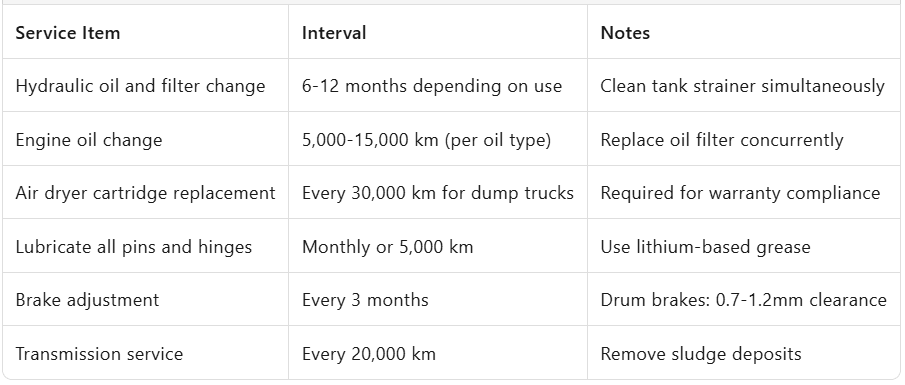
Hydraulic System Care
- Contamination prevention: The leading cause of hydraulic failure. Filter all additions; clean tanks and replace return filters regularly
- Cavitation prevention: Maintain adequate tank levels to prevent pump damage
- Leak management: Inspect seals regularly. High-pressure leaks can inject oil through skin—seek immediate medical attention if this occurs
Section 7: Safety Culture—The Final Layer of Protection
No equipment replaces human judgment:
- Never work under a raised bed without mechanical support: Always use a dump box lock bar before entering beneath the trailer
- Never drive with the bed raised: This drastically alters center of gravity and invites rollover
- Never overload or unevenly load: The primary cause of tip-overs
- Maintain safety zones: Keep all personnel and vehicles at least 10 meters away during unloading
- Continuous training: Conduct regular safety refreshers and emergency drills
Conclusion
The end dump trailer is a powerful productivity tool that demands respect. Proper operating habits, systematic maintenance, and vigilant safety awareness form the tripod of efficient, profitable, and safe operations. Whether you're a veteran driver or fleet manager, treating these guidelines as non-negotiable standards protects your equipment investment, your cargo, and most importantly, the operators who make the industry move.
References:
Pennsylvania Commercial Driver's Manual
- Texas Workers' Compensation Commission Dump Truck Safety Guidelines
- National Ag Safety Database Technical Resources
- Shaanxi Heavy Duty Truck Warranty Manual (2021)
- Industry Technical Literature and Service Manuals
